URL Encode/Decode
Content Editor
URL Encode Result:
URL Decode Result:
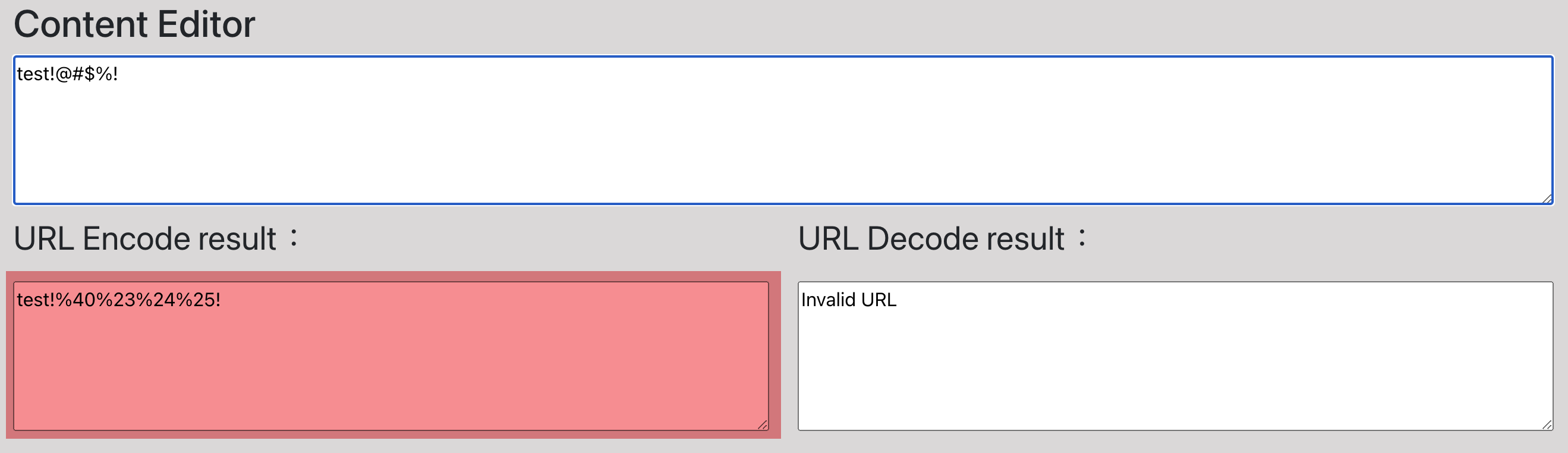
Url Encode Use Example
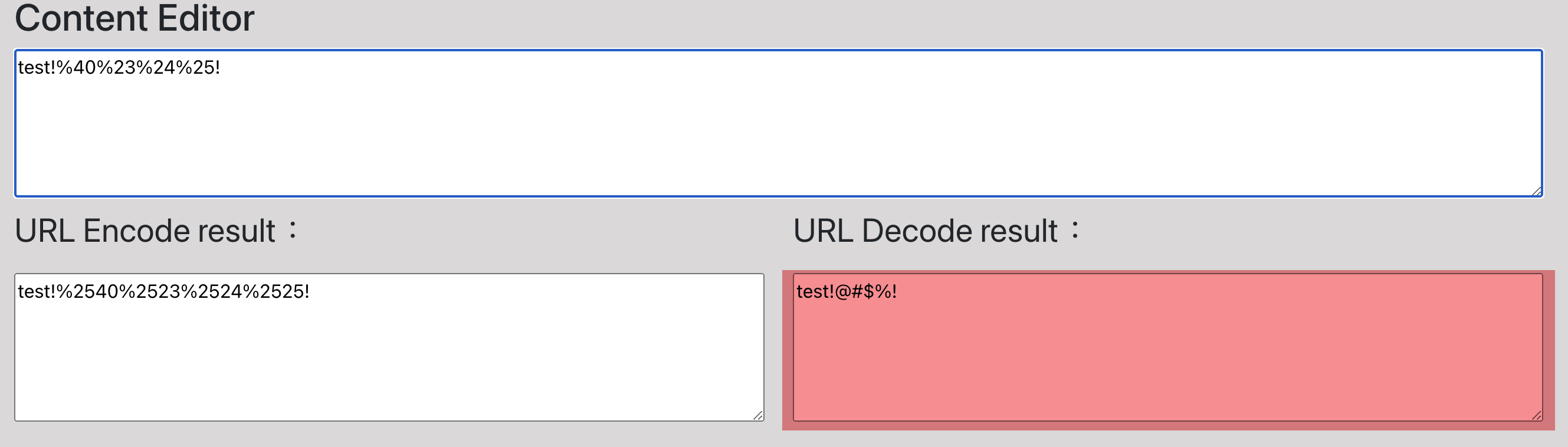
Url Decode Use Example
Encoding Table
| Symbol | URL Encode | .NET URLEncode |
|---|---|---|
| - | %2d | – |
| _ | %5f | _ |
| . | %2e | . |
| @ | %40 | %40 |
| # | %23 | %23 |
| $ | %24 | %24 |
| % | %25 | %25 |
| ^ | %5e | %5e |
| & | %26 | %26 |
| = | %3d | %3d |
| + | %2b | %2b |
| ; | %3b | %3b |
| ? | %3f | %3f |
| / | %2f | %2f |
| \ | %5c | %5c |
| > | %3e | %3e |
| < | %3c | %3c |
| % | %25 | %25 |
| ` | %60 | %60 |
| [ | %5b | %5b |
| ] | %5d | %5d |
| { | %7b | %7b |
| } | %7d | %7d |
| : | %3a | %3a |
| ‘ | %27 | %27 |
| “ | %22 | %22 |
| , | %2c | %2c |
| | | %7c | %7c |
What is Url Encode / Decode?
Percent-encoding, also known as URL encoding, is an encoding mechanism for Uniform Resource Locators (URL) in specific contexts. It is also applicable to Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI) encoding. It is also used to prepare data for 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' MIME, as it is used to submit HTML form data via HTTP requests.
Characters allowed in a URI are divided into reserved and unreserved. Reserved characters have special meanings. For example, the slash character is used as a separator in different parts of a URL (or more generally, a URI). Unreserved characters do not have these special meanings. Percent-encoding represents reserved characters as special character sequences. These situations may vary slightly depending on different versions of URI specifications.