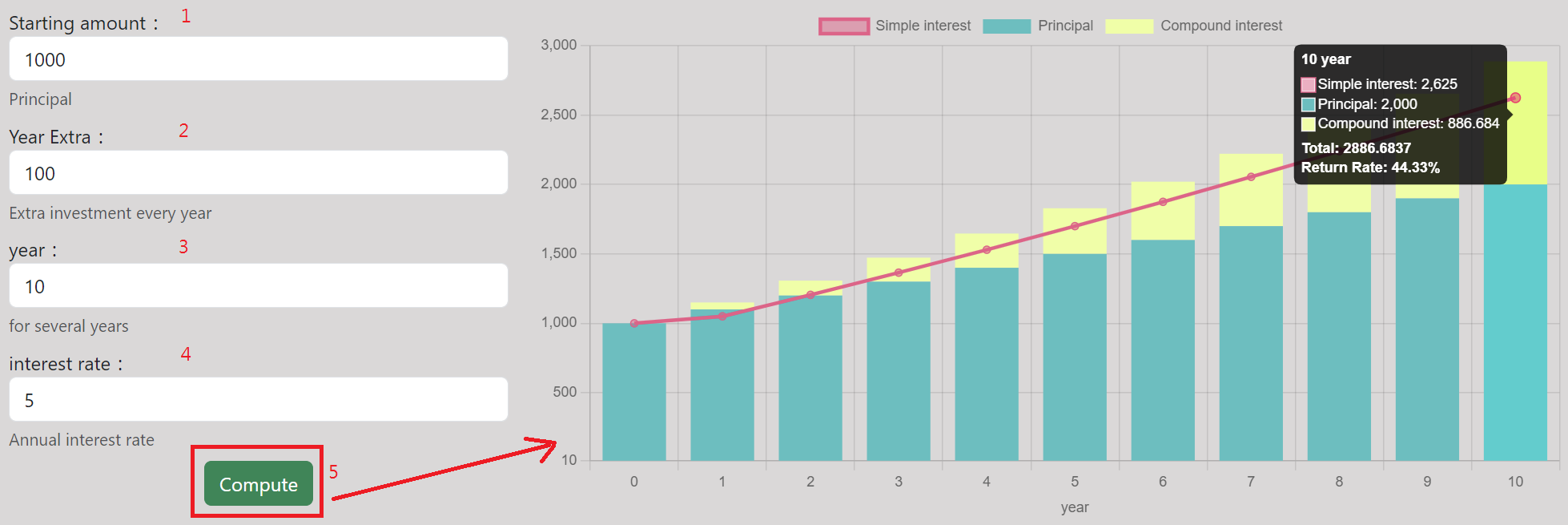
Compound Interest Calculator
- This compound interest calculator shows how your investment grows over time.
- With our compound interest calculator, you can visualize the powerful effect of compound interest and see how your investments and savings grow steadily over time.
Final Result
Principal
0
Compound interest
0
Total Amount
0
Total Return Rate
0%
Use Example
What is compound interest?
Compound interest is a financial calculation method that not only calculates the interest generated by your principal but also adds these interests to the principal to calculate new interest, creating a snowball effect.
Compound Interest Formula Analysis
FV = PV(1 + i)n
FV (Future Value): The expected value of your investment at a future point in time.
PV (Present Value): Your current investment amount or principal.
i: Annual interest rate or expected annual return rate.
n: Investment period, usually in years.
The Power of Compound Interest
Example: Principal 100, annual interest rate 20%.
| First Year | Second Year | Third Year | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound interest | 100 * (1+20%) = 120 | 120 * (1+20%) = 144 | 144 * (1+20%) = 173 |
| Simple interest | 100 + (100*20%) = 120 | 120 + (100*20%) = 140 | 140 + (100*20%) = 160 |
From this example, we can see that the effect of compound interest strengthens over time. The investment return in the second year is 4 more than the first year, and the third year is 13 more than the second year. This is the power of compound interest - your investment returns get better and better over time.